by Kyojin Hwang
📚카테고리 (Category)
📌 Prototype
Prototype이란?🧐
- 자바스크립트의 모든 객체는 자신의
부모 역할을 담당하는객체와 연결되어 있다. 그리고 이것은 마치객체 지향의 상속 개념과 같이 부모 객체의프로퍼티또는메소드를상속받아 사용할 수 있게 한다.
이러한 부모 객체를Prototype(프로토타입) 객체또는 줄여서Prototype(프로토타입)이라 한다.
// prototype
// 잠깐 리터럴이란?🧐
// 리터럴은 데이터(값) 그 자체를 뜻한다. 즉, 변수에 넣는 변하지 않는 데이터를 의미하는 것.
// 객체리터럴, 배열리터럴 등등 여러가지가 있다.
// 여기서 fruits 는 new Array를 통한 instance 이다.
const fruits = new Array("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
console.log(fruits); // (3) ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
console.log(fruits.length); // 3
console.log(fruits.includes("Banana")); // true
console.log(fruits.includes("Melon")); // false
// 프로토타입 속성에서 우리가 인위적으로 만드는 어떤 메소드는
// 기본적으로 function 키워드를 사용하는 일반 함수를 써준다.
Array.prototype.kyojin = function () {
console.log(this); // this는 fruits를 가리킨다.
};
fruits.kyojin(); // (3) ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
const arr = ["order"];
arr.kyojin(); // ['order]
--------------------------------------------------
// 🔊 리터럴 방식
const owen1 = {
firstName: "Owen",
lastName: "Cold",
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
},
};
const kyo1 = {
firstName: "Kyo",
lastName: "Jin",
};
// kyo는 owen 이라는 리터럴객체에서 getFullName을 빌려썻다.
console.log(owen1.getFullName.call(kyo1)); // Kyo Jin
// 🔊 생성자 함수 방식
function User(first, last) {
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
}
// 프로토타입에 공통함수 적용
User.prototype.getFullName = function () {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
};
const owen2 = new User("Owen", "Cold");
const kyo2 = new User("Kyo", "Jin");
console.log(owen2);
console.log(kyo2);
console.log(owen2.getFullName());
console.log(kyo2.getFullName());
📌 Class 기본문법
Class란?🧐
- 클래스의 이름은
Korea와 같이 대문자로 시작한다. - 클래스는 반드시 정의한 뒤에 사용할 수 있다.
- 클래스 내에 정의된 함수를
method라고 부른다 - 클래스를 통해 생성된 객체를
인스턴스(instance)라고 부른다. ex) 인스턴스 = new Class()
prototype
function User(first, last) {
this.fristName = first
this.lastName = last
}
User.prototype.getFullName = function () {
return `${this.fristName} ${this.lastName}`
}
const kyo = new User('Kyo', 'Jin')
const owen = new User('Owen', 'Cold')
console.log(kyo) // User {firstName: 'Kyo', lastName: 'Jin'}
console.log(owen) // User {firstName: 'Owen', lastName: 'Cold'}
console.log(kyo.getFullName()) // Kyo Jin
console.log(owen.getFullName()) // Owen Coldclass
class User {
// constructor 는 위의 프로토타입에 function User 역할을 한다
constructor(first, last) {
this.firstName = first
this.lastName = last
}
// 쉼표를 쓰지않고 함수를 바로 작성한다.
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`
}
}
const kyo = new User('Kyo', 'Jin')
const owen = new User('Owen', 'Cold')
console.log(kyo) // User {firstName: 'Kyo', lastName: 'Jin'}
console.log(owen) // User {firstName: 'Owen', lastName: 'Cold'}
console.log(kyo.getFullName()) // Kyo Jin
console.log(owen.getFullName()) // Owen Cold📌 Getter, Setter
Getter와 Setter 은 함수 호출 형식이 아닌, 일반 프로퍼티처럼 접근해서 사용된다.
예시1
- New라는 키워드를 통해서 생성자 함수로 예시의 User클래스를 호출할 때 최초로 만들어지고 그 다음부터는 firstName과 lastName이 바뀌더라도 전혀 변화가 되지않는다.
class User {
constructor(first, last) {
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
this.fullName = `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
}
const kyo = new User("Kyo", "Jin");
console.log(kyo); // User {firstName: 'Kyo', lastName: 'Jin', fullName: 'Kyo Jin'}
console.log(kyo.getFullName()); // Kyo Jin
kyo.firstName = "Show";
// fullName이 바뀌지않는다. 그래서 getFullName의 메소드를 사용한다.
console.log(kyo); // User {firstName: 'Show', lastName: 'Jin', fullName: 'Kyo Jin'}
console.log(kyo.getFullName()); // Show Jin
예시1을 업그레이드하기 위한 Getter Setter
class User {
constructor(first, last) {
this.firstName = first
this.lastName = last
}
get fullName() {
console.log('Getting full name!')
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`
}
set fullName(value) {
;[this.firstName, this.lastName] = value.split(' ')
}
}
const kyo = new User('Kyo', 'Jin')
console.log(kyo.fullName) // Kyo Jin
kyo.firstName = 'Show'
console.log(kyo.fullName) // Show Jin
kyo.fullName = 'Show Me'
console.log(kyo.fullName) // Show Me
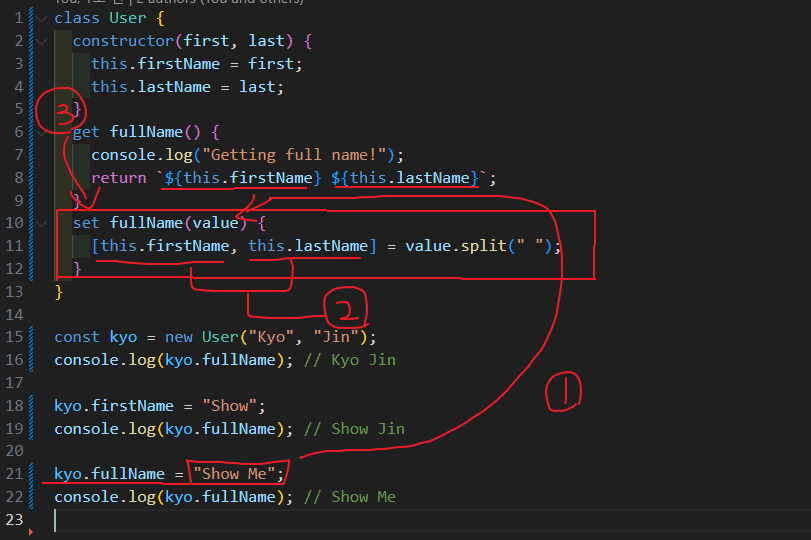
예시1 업그레이드 사진설명
- 21번코드줄에서의
kyo.fullName = "Show Me"는 setfullName에 value로 들어간다. - 배열 구조분해할당으로 인해 this.firstName에는
Showthis.lastName에는Me가 들어간다. - 22번코드줄에서의 fullName은 getfullName이 되며 아래의 set을 조회한다.
Setter의 무한루프
- 접근자 프로퍼티의 이름을 중복이 되도록 하면 안된다.
const user = {
name: "kyo",
get name() {
return user.name;
},
set name(value) {
user.name = value;
},
};
// user 객체의 name 프로퍼티 값을 변경
user.name = "owen";
// Error : Uncaught RangeError RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
-------------------------------------------------
const user = {
_name: "kyo",
get name() {
return user._name;
},
set name(value) {
user._name = value;
},
};
// user 객체의 name 프로퍼티 값을 변경
user._name = "owen";
console.log(user.name); // owen📌 정적메소드
정적 메소드란?🧐
정적 메소드는클래스로 호출한다 vs프로토타입 메소드는인스턴스로 호출한다.
클래스 vs 인스턴스 메소드 차이
class Phone {
constructor(number) {
this.myNumber = number
}
introduce() {
return console.log('프로토타입 메소드')
}
static isComplain() {
return console.log('정적 메소드')
}
}
// 인스턴스 생성
const user = new Phone(7788)
// 클래스
Phone.isComplain()
// 인스턴스
user.introduce()static 사용법
class User {
constructor(first, last) {
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
}
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
// 직접적으로 사용하는 메소드를 만들고 싶을떄는 static
static isUser(user) {
return true;
}
}
const kyo = new User("Kyo", "Jin");
const owen = new User("Owen", "Cold");
console.log(kyo.getFullName()); // Kyo Jin
console.log(owen.getFullName()); // Owen Cold
console.log(User.isUser()); // true
console.log(kyo.isUser()); // Error User에서만 사용가능
-------------------------------------------------
//static isUser 정적메소드를 조금 더 잘 사용해보기
class User {
constructor(first, last) {
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
}
getFullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
// 직접적으로 사용하는 메소드를 만들고 싶을떄는 static
static isUser(user) {
if (user.firstName && user.lastName) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
const kyo = new User("Kyo", "Jin");
const owen = new User("Owen", "Cold");
const roy = {
name: "Roy Wing",
age: 23,
};
console.log(User.isUser(kyo)); // true
console.log(User.isUser(owen)); // true
// first, last Name 이없어서
console.log(User.isUser(roy)); // false
📌 상속과 instanceof
상속
클래스 확장하기: extends 키워드를 사용하여 확장한다.생성자 오버라이딩: this를 사용하기 전에 Child 생성자 안에서 super()로 부모 생성자를 반드시 호출해야 합니다.
예제
inheritance.js
// 상속(Inheritance)
// 운송수단
class Vehicle {
constructor(acceleration = 1) {
this.speed = 0
this.acceleration = acceleration
}
accelerate() {
this.speed += this.acceleration
}
decelerate() {
if (this.speed <= 0) {
console.log('정지!')
return
}
this.speed -= this.acceleration
}
}
// 자전거
class Bicycle extends Vehicle {
constructor(price = 100, acceleration) {
// super는 Vehicle의 constructor 과 같다.
super(acceleration)
this.price = price
this.wheel = 2
}
}
const bicycle = new Bicycle(300)
bicycle.accelerate() // 가속! 10
bicycle.accelerate() // 가속! 20
console.log(bicycle) // Bicycle {speed: 2, acceleration: 1, price: 300, wheel: 2}
console.log(bicycle instanceof Bicycle) // true
console.log(bicycle instanceof Vehicle) // true
// 자동차
class Car extends Bicycle {
constructor(license, price, acceleration) {
super(price, acceleration)
this.license = license
// 자전거의 wheel을 4로 덮는다.
this.wheel = 4
}
accelerate() {
if (!this.license) {
console.log('무면허!')
return
}
this.speed += this.acceleration
console.log('가속!', this.speed)
}
}
const carA = new Car(true, 7000, 10)
const carB = new Car(false, 4000, 6)
carA.accelerate() // 가속! 10
carA.accelerate() // 가속! 20
carB.accelerate() // 무면허!
console.log(carA) // Car {speed: 20, acceleration: 10, price: 7000, wheel: 4, license: true}
console.log(carB) // Car {speed: 0, acceleration: 6, price: 4000, wheel: 4, license: false}
// 보트
class Boat extends Vehicle {
constructor(price, acceleration) {
super(acceleration)
this.price = price
this.motor = 1
}
}
const boat = new Boat(3000, 5)
console.log(boat) // Boat {speed: 0, acceleration: 5, price: 3000, motor: 1}instanceof
- 키워드 앞쪽에 있는 데이터가 키워드 뒤쪽에 있는 클래스에서 인스턴스로 만들어져 있는지 확인하는 것
예제
instanceofEx.js
class Rabbit {}
const rabbit = new Rabbit()
console.log(rabbit instanceof Rabbit) // true
// Array 내장 클래스에서 사용하는법
let arr = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(arr instanceof Array) // true
console.log(arr instanceof Object) // true📌 instanceof 와 constructor (Class 상속)
예제
classEx.js
class A {
constructor() {}
}
class B extends A {
constructor() {
super()
}
}
class C extends B {
constructor() {
super()
}
}
const a = new A()
const b = new B()
const c = new C()
console.log(c instanceof A) // true
console.log(c instanceof B) // true
console.log(c instanceof C) // true
console.log(c.constructor === A) // false
console.log(c.constructor === B) // false
console.log(c.constructor === C) // true
// fruits는 Array라는 클래스의 인스턴스 이다.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana']
console.log(fruits.constructor === Array) //true